Assume the reaction A + B → C + D proceeds to equilibrium. Calculate the equilibrium concentration of D at  given that the starting concentrations of A and B are 2M and that △G° for the reaction is
given that the starting concentrations of A and B are 2M and that △G° for the reaction is 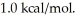
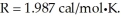
Definitions:
Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis involves evaluating the financial statements of a company to assess its performance and make informed business decisions.
IRS Audit
A formal examination by the Internal Revenue Service to verify the accuracy of a taxpayer's returns and financial records.
Current Ratio
A liquidity ratio that measures a company's ability to pay short-term obligations with its current assets.
Price-earnings Ratio
A valuation ratio of a company's current share price compared to its per-share earnings, used to gauge if a stock is over- or under-valued.
Q1: A patient is being weaned from parenteral
Q8: A patient is admitted to a patient
Q9: Which of the following steps would successfully
Q12: A 68-year-old female patient has had a
Q21: Which of the following amino acids are
Q33: Draw the Newman projection of the anti
Q48: Is the molecule shown below chiral or
Q54: Provide the structure of L-aspartic acid at
Q63: Which of the following reagents are commonly
Q97: Predict the major monobromination product in the