The addition of either the methyl Grignard reagent or methyllithium to camphor,followed by hydrolysis,produces a tertiary alcohol known as 2-methylisoborneol,an algal metabolite which imparts a musty odor to water at very low concentrations.However,the yield of alcohol does not exceed 50%,and large amounts of camphor are recovered from the reaction even when a large excess of the Grignard or lithium reagent are used.What would be the most plausible explanation? 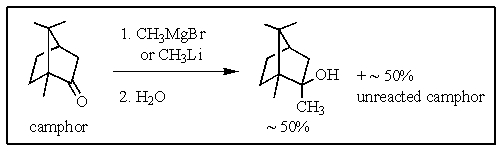
Definitions:
Cognitive Developmental Stages
Theoretical stages proposed by psychologists to describe the progression of thinking and reasoning abilities as people grow.
Conceptual Frameworks
Structures of concepts and ideas that guide thinking, research, and practice in various fields by providing an organized way to make sense of related phenomena.
Piaget
A Swiss psychologist known for his pioneering work in child development, specifically his theory of cognitive development that describes how children construct a mental model of the world.
Formal Operational Stage
In Piaget’s theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts.
Q4: What is the correct structure of 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene?<br>A)<br><img
Q11: Which of the following is considered to
Q15: D-(+)-Glucose and D-(+)-Mannose have the same molecular
Q18: Which of the following represents how a
Q18: Which of the following is referred to
Q21: What would be the expected product of
Q23: Which of the following dienes would you
Q23: Which of the following could have both
Q30: The common name for 1-methylpropyl is:<br>A) Isopropyl<br>B)
Q35: How many chiral centers are present in