The proton NMR spectrum of a carboxylic acid,C13H18O2,commonly sold as an over-the-counter headache remedy,is shown below.Note: the CO2H proton is not shown,and the multiplicity of the peaks are noted (d = doublet,q = quartet,m = multiplet) .Which structure is that of this pharmaceutical? 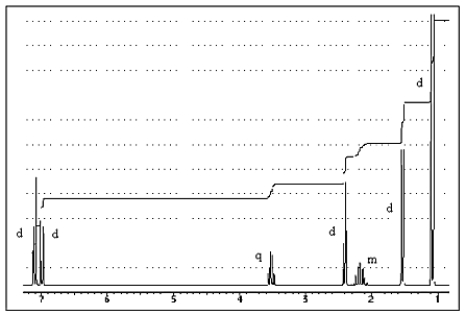
Definitions:
Type I Error
Type I error, often denoted as α, occurs when a true null hypothesis is incorrectly rejected, indicating a false positive finding in hypothesis testing.
Null Hypothesis
A statement suggesting that there is no significant difference or relationship between specified populations, any observed effect being due to sampling or experimental error.
Type I Error
The mistake of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true, commonly referred to as a "false positive."
Type II Error
The error that occurs when a false null hypothesis is not rejected.
Q4: The following is an example of intramolecular
Q6: The nitrogen of trimethylamine [(CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>3</sub>N] contains how
Q8: What product do you expect from the
Q12: In order of decreasing reactivity,how would the
Q12: What reactants would be required to prepare
Q19: Which of the following would be properly
Q21: Indicate to which side,if any,the following equilibrium
Q28: Predict the product of the following reaction:
Q33: Which reagents would you expect to accomplish
Q37: What would be the proper name of