In the robotics industry there are 100 firms. Each firm shares the same long-run cost function. It is: C(q) = 100 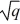
. The relevant marginal cost function is MC(q) = 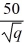
. Each of the 100 firms produce 64 units. The market demand for robotics is: QD = 15,000 - 688P. Calculate the market price at this production level. Also, calculate the profits for a representative firm in the robotics industry. If one firm expanded production to 100 units while the remaining 99 firms kept output at 64 units, what would happen to the market price and profits? Would all firms benefit or lose if every firm expanded output to 100 units?
Definitions:
Equilibrium Price
The price point at which the quantity of goods supplied equals the quantity demanded, resulting in market balance.
Equilibrium Quantity
At the equilibrium price, the volume of goods or services both offered and sought.
Quantity Supplied
The amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price level in a given time period.
Equilibrium Price
The point at which the demand for a particular good or service matches its supply, ensuring equilibrium in the market.
Q1: A boundary surrounds the system and _
Q27: Murray Manufacturing Company produces pantyhose. The firm's
Q29: List and define the three interrelated components
Q32: A competitive market is made up of
Q67: Bette's Breakfast, a perfectly competitive eatery, sells
Q131: Sarah's Pretzel plant has the following short-run
Q148: An increasing-cost industry is so named because
Q154: The market for semiskilled labor can be
Q157: Use the following two statements to answer
Q163: Farmer Jones bought his farm for $75,000