Mel and Christy are co-workers with different risk attitudes. Both have investments in the stock market and hold U.S. Treasury securities (which provide the risk free rate of return). Mel's marginal rate of substitution of return for risk ( 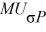
/ MU RP, σP) is
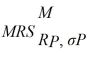
= 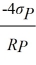
where RP is the individual's portfolio rate of return and σP is the individual's portfolio risk. Christy's 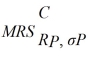
= 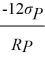
. Each co-worker's budget constraint is RP = RF + 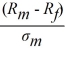
σP, where Rj is the risk-free rate of return, Rm is the stock market rate of return, and σm is the stock market risk. Solve for each co-worker's optimal portfolio rate of return as a function of Rj, Rm, and σm.
Definitions:
Real Balances
Real balances refer to the purchasing power of money holdings, adjusted for changes in the price level, indicating how much can be bought with a given amount of money.
Line Segment QR
A part of a line that is bounded by two distinct end points, Q and R, and contains every point on the line between Q and R.
Unemployed Resources
Factors of production that are available for use but are not currently engaged in the production of goods or services.
Keynesian Model
An economic theory stating that government intervention through fiscal policies is necessary to moderate the boom and bust cycles of an economy.
Q2: The income elasticity of demand is the<br>A)
Q7: If the actual price were below the
Q21: The total cost of producing a given
Q37: The monthly supply of desktop personal computers
Q49: If an Engel curve has a negative
Q80: C and S Metal Company produces stainless
Q119: Suppose the long-run cost function is C
Q125: Michael's dairy farm's cost function is C(q)
Q128: Jonathan and Roberto enjoy playing poker. Jonathan's
Q153: See Scenario 4.5. The Engel curve for