Mr. Barnes has a monopoly in the production of power in the local market. The demand for Mr. Barnes power is: 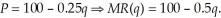 Mr. Barnes marginal costs are constant at 5. In the generation of power, Mr. Barnes plant emits pollution that causes marginal external damages according to:
Mr. Barnes marginal costs are constant at 5. In the generation of power, Mr. Barnes plant emits pollution that causes marginal external damages according to: 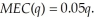 If the local government does nothing, how much will Mr. Barnes produce to maximize profits? What is the marginal social cost of his level of output? What price do consumers pay for each unit of Mr. Barnes' output? Is this level of production optimal? Should the local government institute a pollution fee? If so, what is the optimal fee?
If the local government does nothing, how much will Mr. Barnes produce to maximize profits? What is the marginal social cost of his level of output? What price do consumers pay for each unit of Mr. Barnes' output? Is this level of production optimal? Should the local government institute a pollution fee? If so, what is the optimal fee?
Definitions:
Void
Describes a contract or legal agreement that lacks validity and enforceability from the outset.
Economic Duress
Coercion involving threats to a person’s business or financial condition that compel the person to act against their will in entering a contract.
Voluntary Choice
The concept of making decisions freely, without coercion, often discussed in contexts of contract law and ethics.
Legitimate Alternatives
Viable and lawful options or solutions that are considered acceptable within a given context or situation.
Q13: Prices in the world's financial markets are
Q24: Opportunities for MNCs to create value through
Q26: Refer to Figure 16.2.3 above. The initial
Q27: Canada produces MP3 players and lumber, and
Q40: Consider a potential, voluntary exchange between two
Q43: At the expiration of a futures contract,
Q83: Over time, endowment effects tend to:<br>A) disappear,
Q84: The city of Econoville has 100 residents
Q86: The higher the beta,<br>A) the smaller the
Q112: XYZ Corporation will pay the $1,000 face