The long-run cost function for LeAnn's telecommunication firm is: 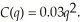 A local telecommunication tax of $0.01 has been implemented for each unit LeAnn sells. This implies the marginal cost function becomes:
A local telecommunication tax of $0.01 has been implemented for each unit LeAnn sells. This implies the marginal cost function becomes: 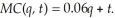 If LeAnn can sell all the units she produces at the market price of $0.70, calculate LeAnn's optimal output before and after the tax. What effect did the tax have on LeAnn's output level? How did LeAnn's profits change?
If LeAnn can sell all the units she produces at the market price of $0.70, calculate LeAnn's optimal output before and after the tax. What effect did the tax have on LeAnn's output level? How did LeAnn's profits change?
Definitions:
Fee-For-Service
A payment model where services are unbundled and paid for separately, often leading to higher healthcare costs but greater flexibility for patients.
Salary
Regular payment made by an employer to an employee, usually monthly or biweekly, for their professional services.
Single Payer System
A healthcare system where a single public or quasi-public agency organizes healthcare financing, but delivery of care remains largely private.
Health Care Costs
Expenses related to medical care, including the cost of procedures, services, drugs, and equipment needed for the treatment and well-being of individuals.
Q2: The amount of output that a firm
Q6: Where Es is the elasticity of supply
Q19: In an increasing-cost industry, expansion of output:<br>A)
Q22: At the profit-maximizing level of output, marginal
Q39: Refer to Figure 9.2.1 above. When the
Q68: Marginal profit is equal to<br>A) marginal revenue
Q73: What is the value of the Lerner
Q83: Assume that average product for six workers
Q104: Tad's Baitshop currently uses no computers in
Q127: Refer to Figure 7.2.1 above. The diagram