Sandra lives in the Pacific Northwest and enjoys walking to and from work during sunny days. Her utility is sharply diminished if she must walk while it is raining. Sandra's utility function is 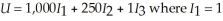 if she walks and there is no rain and
if she walks and there is no rain and 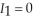 otherwise,
otherwise, 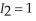 if she drives to work and
if she drives to work and 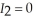 otherwise, and
otherwise, and 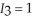 if she walks and it rains and
if she walks and it rains and 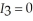 otherwise. Sandra believes that the probability of rain today is 3/10. Given her beliefs, what is her expected utility from walking to work? What is her expected utility from driving to work according to her beliefs? If Sandra maximizes her expected utility according to her beliefs, will she drive or walk to work? Sandra missed the weather report this morning that stated the true probability of rain today is 4/5. Given the weather report is accurate, what is Sandra's true expected utility from walking and driving to work? How much could Sandra increase her expected utility if she read and believed the weather report?
otherwise. Sandra believes that the probability of rain today is 3/10. Given her beliefs, what is her expected utility from walking to work? What is her expected utility from driving to work according to her beliefs? If Sandra maximizes her expected utility according to her beliefs, will she drive or walk to work? Sandra missed the weather report this morning that stated the true probability of rain today is 4/5. Given the weather report is accurate, what is Sandra's true expected utility from walking and driving to work? How much could Sandra increase her expected utility if she read and believed the weather report?
Definitions:
Real Options
An approach in finance where choices are treated as derivative securities that managers can use to maximise returns while deferring investment decisions.
Expected NPV
An estimation of the Net Present Value of a project or investment, considering the potential outcomes and their probabilities.
Obligation
A legal or financial duty or commitment one party owes to another, often in the form of debts or contractual agreements.
Flexibility Options
Options within contracts or agreements that allow for adjustments based on varying circumstances or needs.
Q9: Use the following two statements to answer
Q18: You view tea and scones as perfect
Q39: Complete the following table (round each answer
Q42: When 1983 is the CPI base year,
Q54: Consider the following statements when answering this
Q56: Alfred derives utility from consuming iced tea
Q64: The battery packs used in electric and
Q96: A curve that represents all combinations of
Q108: Refer to Table 3.1. If preferences satisfy
Q146: If a competitive firm's marginal costs always