Sally consumes two goods, X and Y. Her utility function is given by the expression 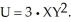 The current market price for X is $10, while the market price for Y is $5. Sally's current income is $500.
The current market price for X is $10, while the market price for Y is $5. Sally's current income is $500.
a. Sketch a set of two indifference curves for Sally in her consumption of X and Y.
b. Write the expression for Sally's budget constraint. Graph the budget constraint and determine its slope.
c. Determine the X,Y combination which maximizes Sally's utility, given her budget constraint. Show her optimum point on a graph. (Partial units for the quantities are possible.) 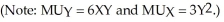 d. Calculate the impact on Sally's optimum market basket of an increase in the price of X to $15. What would happen to her utility as a result of the price increase?
d. Calculate the impact on Sally's optimum market basket of an increase in the price of X to $15. What would happen to her utility as a result of the price increase?
Definitions:
Net Operating Income
An entity’s income after all operating expenses have been deducted from total revenue, excluding taxes and interest charges.
Variable Costing
A costing method in which fixed manufacturing overhead is not assigned to the product, but rather treated as an expense of the period.
Absorption Costing
is an accounting method that includes all manufacturing costs—direct materials, direct labor, and both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead—in the cost of a product.
Unit Product Cost
The total cost incurred to produce, manufacture, or acquire a product, divided by the total number of units produced.
Q4: You are given the following table for
Q16: If the quantity of a good demanded
Q17: Any risk-averse individual would always:<br>A) take a
Q34: Refer to Figure 2.3.1. In Example 2.4,
Q40: Refer to Scenario 5.2. Samantha's expected expense
Q46: The marginal rate of technical substitution is
Q65: Microeconomics is the branch of economics that
Q82: The individual pictured in Figure 5.2.3:<br>A) must
Q82: A system of rationing:<br>A) benefits those with
Q174: When we solve the firm's dual production