Use the following to answer question: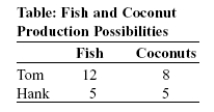
-(Table: Fish and Coconut Production Possibilities) Use Table: Fish and Coconut Production Possibilities.The table shows the maximum number of fish and coconuts that Tom and Hank can produce if they produce only one good.In the absence of trade,Tom produces and consumes 9 fish and 2 coconuts,and Hank produces and consumes 3 fish and 2 coconuts.Now they decide to engage in trade.Which statement is INCORRECT?
Definitions:
Fallacy
A mistaken belief or error in reasoning, often leading to invalid arguments.
False Dichotomy
A logical fallacy that involves presenting two opposing options as the only possibilities, when in fact more options exist.
Hasty Generalization
A logical fallacy in which a conclusion is not logically justified by sufficient or unbiased evidence.
False Alternative
A logical fallacy where only a limited set of options are presented, ignoring other viable alternatives.
Q3: As a result of frequent flooding,the insurance
Q15: Above-equilibrium wages paid by some employers as
Q23: (Table: Price,Quantity Demanded,and Quantity Supplied)Use Table: Price,Quantity
Q35: (Figure: Unemployment Rate over Time)Look at the
Q37: (Table: Natasha's Total Utility)Use Table: Natasha's Total
Q71: A simplified version of reality that is
Q92: (Table: Choice with Uncertainty)Use Table: Choice with
Q117: (Figure: Demand for Coconuts)Use Figure: Demand for
Q122: An increase in demand for good X
Q148: Above-equilibrium wages paid by some employers as