Object A has a position as a function of time given by 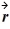 A(t) = (3.00 m/s) t
A(t) = (3.00 m/s) t 
+ (1.00 m/s2) t2

. Object B has a position as a function of time given by 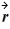
B(t) = (4.00 m/s) t 
+ (-1.00 m/s2) t2

. All quantities are SI units. What is the distance between object A and object B at time 
Definitions:
Dietary Experts
Professionals specialized in nutrition and diet planning to promote health and manage diseases.
Reaction To Catastrophe
Reaction To Catastrophe refers to the wide range of emotional, cognitive, and behavioral responses that individuals and communities exhibit in response to a catastrophic event or disaster.
Recovery Stage
A phase in the healing process of an illness, injury, or psychological condition where symptoms are subsiding and functionality starts to restore.
Recovery Stage
A phase in the healing or rehabilitation process where improvement and return to a normal state or condition occur.
Q5: A 30.0-kg object experiences a drag force
Q7: Wire is wound on a square frame,
Q9: An object is moving to the right,
Q19: A current carrying loop of wire lies
Q21: Scandium, <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4469/.jpg" alt="Scandium, Sc,
Q35: A series circuit consists of ac source,
Q47: An LR circuit contains an ideal 60-V
Q60: One of the uses of the Conceptual
Q62: The maximum permissible workday dose for occupational
Q64: A rectangular coil having N turns and