A projectile is fired from point 0 at the edge of a cliff, with initial velocity components of 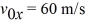
and 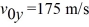
, as shown in the figure.The projectile rises and then falls into the sea at point P. The time of flight of the projectile is 40.0 s, and it experiences no appreciable air resistance in flight. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the projectile 21.0 s after it is fired? 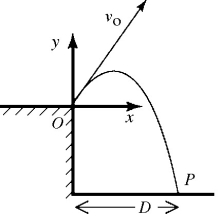
Definitions:
Substrate-Level
Substrate-level refers to a biochemical process that involves the direct transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP to form ATP, bypassing the need for an electron transport chain.
ATP Synthesis
The process by which cells produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a critical energy carrier molecule, primarily in the mitochondria.
ADP
Adenosine diphosphate, a molecule involved in energy transfer within cells.
Exergonic Reaction
Chemical reaction that releases energy; opposite of endergonic reaction.
Q2: Which one of the following free-body diagrams
Q2: The regulation of accounting can be argued
Q5: Criticisms of PAT include.<br>A) It does not
Q7: A box of mass 50 kg is
Q15: If the accuracy in measuring the position
Q21: An atom with 5 electrons is in
Q24: A laser emits light of wavelength 463
Q45: Two space stations are at rest relative
Q49: An electron is bound in an infinite
Q50: Which of the following are considered in