In the figure, a 0.24-kg ball is suspended from a very light string 9.79 m long and is pulled slightly to the left. As the ball swings without friction through the lowest part of its motion it encounters an ideal massless spring attached to the wall. The spring pushes against the ball and eventually the ball is returned to its original starting position. Find the time for one complete cycle of this motion if the spring constant of the spring is 21 N/m. (Assume that once the pendulum ball hits the spring there is no effect due to the vertical movement of the ball.) 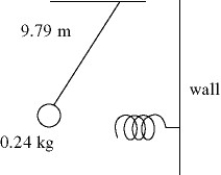
Definitions:
Classical Conditioning
The method by which repeated association of two stimuli results in a response that was initially elicited by the second stimulus being elicited by the first stimulus over time.
Neutral Stimulus
An initially neutral stimulus that doesn't trigger a specific reaction besides drawing attention, until it becomes linked with an unconditioned stimulus.
Conditioned Stimulus
An initially neutral cue that, upon repeated pairing with an unconditioned stimulus, produces a conditioned reaction.
Positive Reinforcement
A process in operant conditioning where introducing a rewarding stimulus following a desired behavior increases the likelihood of that behavior being repeated.
Q3: A bag of potato chips contains 2.00
Q3: A guitar string is fixed at both
Q17: A 5.0-kg block is attached to an
Q25: Neptune circles the Sun at a distance
Q27: The figure represents the position of a
Q28: For the apparatus shown in the figure,
Q37: A woman is riding a bicycle at
Q38: If we double the root-mean-square speed (thermal
Q38: Find the speed of an ocean wave
Q42: A 7.8-kg solid sphere, made of metal