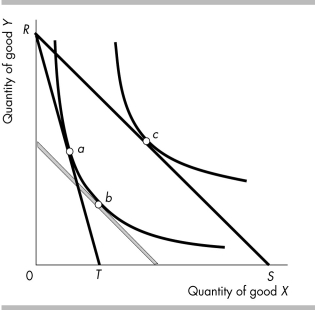
-In the above figure, if the budget line shifts from RT to RS, the substitution effect is illustrated by the move from
Definitions:
Adverse Selection
Adverse selection is a situation in economics where one party in a transaction has more information than the other, often leading to an imbalance and unfavorable outcomes for one side.
Screening
A solution to the problem of adverse selection that describes the efforts of a less informed party to gather information about the more informed party. A successful screen means that it is unprofitable for bad types to mimic the behavior of good types. Any successful screen can also be used as a signal.
Signaling
A solution to the problem of adverse selection that describes an informed party’s effort to communicate her type, risk, or value to less informed parties by her actions. A successful signal is one that bad types won’t mimic. Any successful signal can also be used as a screen.
Anticipate Adverse Selection
The practice of predicting and mitigating the likelihood of selecting undesirable risks due to information asymmetry.
Q4: The profit maximizing condition for any competitive
Q7: The table above shows the total utility
Q16: Kumiko is not at her consumer equilibrium
Q140: Utility is best defined as<br>A) the amount
Q153: Steve has two goods he can spend
Q182: If the price of a good increases,
Q194: For a consumer, the marginal utility of
Q297: The indifference curve in the above figure<br>A)
Q351: Suppose the price of soda is $2
Q377: Given the budget line in the above