Two loudspeakers placed 6.0 m apart are driven in phase by an audio oscillator whose frequency range is 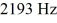 to
to 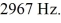 A point P is located
A point P is located 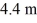 from one loudspeaker and 3.6 m from the other.The speed of sound is 344 m/s.The frequency produced by the oscillator,for which constructive interference of sound occurs at point P,is closest to
from one loudspeaker and 3.6 m from the other.The speed of sound is 344 m/s.The frequency produced by the oscillator,for which constructive interference of sound occurs at point P,is closest to
Definitions:
Intravenous Pyelography
A radiographic imaging technique used to visualize the kidneys, ureters, and bladder by introducing a contrast medium intravenously.
KUB
An acronym for Kidney, Ureter, and Bladder, referring to an X-ray imaging technique focusing on these abdominal areas.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging; a medical imaging technique used to visualize internal structures of the body in detail, using magnetic fields and radio waves.
CT
Computerized Tomography, a medical imaging technique that combines multiple X-ray measurements taken from different angles to produce cross-sectional images of specific areas of a scanned object.
Q9: A slender uniform rod 100.00 cm long
Q9: A point charge Q = -500 nC
Q10: A 7.8-kg solid sphere,made of metal whose
Q14: A nonuniform electric field is directed along
Q24: A 2.5-kg box,sliding on a rough horizontal
Q26: The resistivity of gold is <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4470/.jpg"
Q32: An object of mass 4.0 kg starts
Q34: 50)A 0.25-m string,vibrating in its sixth harmonic,excites
Q35: A hollow steel ball of diameter 3.0
Q70: 3.0 moles of an ideal gas with