The shaded block in the table below shows the amount of output that can be produced using different combinations of labor and capital in a hypothetical economy with a given type of technology. For example, 1,200 units of output are produced when 75 units of labor and 75 units of capital are combined. This table is an example of a production function. 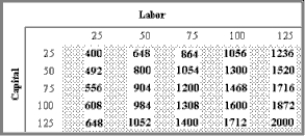 (A)Hold capital constant at 50 while you increase labor. What happens to output?
(A)Hold capital constant at 50 while you increase labor. What happens to output?
(B)Now hold labor constant at 50 and raise the level of capital. What happens to output?
(C)Finally, what happens to output when labor and capital are raised by the same amount, assuming that you start with 50 units of each?
(D)Sketch the production function on a graph that plots labor on the horizontal axis and output on the vertical axis. Assume capital is fixed at 50. What happens to the graph if capital is increased to 100?
(E)What happens to the output numbers in the table if there is an improvement in technology? What would happen to your graph in part (D)?
Definitions:
Net Income
An entity's earnings after all expenses, including taxes and operating costs, have been deducted from revenues.
Physical Inventory
The process of counting and verifying the actual quantities of merchandise or goods in stock.
Absorption Cost
An accounting method that assigns all manufacturing costs (both fixed and variable) to products, making them fully absorbed into the cost of goods sold.
Fixed Overhead
The portion of a company's fixed costs that are not directly tied to production levels, such as rent and insurance.
Q20: With a single supply and demand diagram,
Q81: For the hypothetical economy described in the
Q90: Which of the following statements is true?<br>A)
Q93: The term quantity supplied refers to<br>A) the
Q96: Simon Kuznets won a Nobel Prize in
Q104: The largest component of GDP is<br>A) government
Q113: Using 2011 prices, according to the data
Q143: An increase in taxes will not affect
Q146: If the exchange rate becomes less sensitive
Q150: Determine in which spending category, if any,