An operations manager's staff has compiled the information below for four manufacturing alternatives (E, F, G, and H) that vary by production technology and the capacity of the machinery. All choices enable the same level of total production and have the same lifetime. The four states of nature represent four levels of consumer acceptance of the firm's products. Values in the table are net present value of future profits in millions of dollars. Forecasts indicate that there is a 0.1 probability of acceptance level 1, 0.2 chance of acceptance level 2, 0.4 chance of acceptance level 3, and 0.3 change of acceptance level 4.
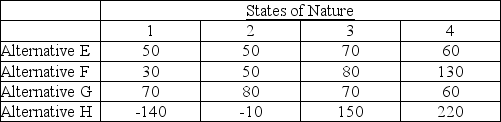 Using the criterion of expected monetary value, which production alternative should be chosen?
Using the criterion of expected monetary value, which production alternative should be chosen?
Definitions:
Lot Sizing Decisions
The process of determining the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs, including ordering, holding, and stockout costs.
Fixed Costs
Expenses that do not change in the short term, regardless of the level of production or sales activities, such as rent, salaries, and insurance.
Quantity Discounts
Reductions in price per unit based on the amount of goods purchased, used as an incentive for buyers to purchase larger quantities.
Price Discounts
Reductions in the selling price of goods or services, often used as a strategy to increase sales volume and attract customers.
Q1: _ avoids placing materials or supplies in
Q15: Which of the following methods best considers
Q16: A transportation model uses only 5% of
Q46: Design capacity is the theoretical maximum output
Q55: A good capacity decision requires that it
Q61: Industrial firms choose locations that minimize cost,
Q76: The likelihood that a decision maker will
Q93: The theory of constraints has its origins
Q102: The typical full-service restaurant uses a product-focused
Q133: One guideline for determining the arrangement and