Byron's Manufacturing makes tables. Demand for the next four months and capacities of the plant are shown in the table below. Unit cost on regular time is $40. Overtime cost is 150% of regular time cost. Subcontracting is available in substantial quantity at $75 per unit. Holding costs are $5 per table per month; back orders cost the firm $10 per unit per month. Byron's management believes that the transportation algorithm can be used to optimize this scheduling problem. The firm has 50 units of beginning inventory and anticipates no ending inventory.
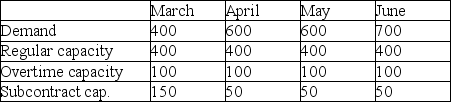 a. How many units will be produced on regular time in June?
a. How many units will be produced on regular time in June?
b. How many units will be produced by subcontracting over the four-month period?
c. What will be the inventory at the end of April?
d. What will be total production from all sources in April?
e. What will be the total cost of the optimum solution?
f. Does the firm utilize the expensive options of subcontracting and back ordering? When; why?
Definitions:
Disease-causing Organisms
Microorganisms or pathogens that can lead to diseases in their hosts, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Salmonella
A group of bacteria that can cause foodborne illness, typically resulting from consuming contaminated food or water.
Noroviruses
A group of viruses that are a leading cause of gastrointestinal illness, including stomach flu.
Energy Balance
The equilibrium between calories consumed through food and beverages and calories expended through physical activity and metabolic processes.
Q21: Savings in the supply chain exert more
Q32: Nearsourcing helps compromise a company's desire for
Q32: Labor standards are defined as the<br>A) preset
Q53: Which of the following dispatching rules tends
Q76: Which scheduling technique should be employed when
Q76: Daily usage of an assembly is 100
Q81: Name three common things that contribute to
Q119: What is DRP?
Q168: Normal time for a stopwatch study is
Q190: A manufacturing plant allows its engineers to