Pipeline fluid flows are indicated below. Determine the maximum flow from Node 1 to Node 4. 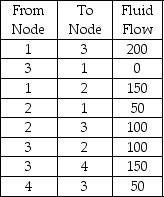
Definitions:
Exponential Random Variable
A type of continuous random variable that is used to model time until an event occurs, with a constant hazard rate.
Exponential Distribution
A continuous probability distribution that describes the times between events in a Poisson process, representing a constant hazard rate.
Density Function
A mathematical function that describes the distribution of a continuous random variable, indicating the probability of the variable falling within a particular range.
Exponentially Distributed
Pertaining to a statistical distribution characterized by a constant rate of decay or growth over time.
Q23: Determining the mixture of ingredients for a
Q24: In the term linear programming, the word
Q37: A point in the network, that is
Q38: The maximal-flow technique would be helpful to
Q45: According to Table 8-1, which describes a
Q49: Given an activity's optimistic, most likely, and
Q54: The condition when there is no solution
Q64: Which of the following methods is used
Q79: Suppose a linear programming (minimization) problem has
Q116: A(n) _ state is the normal operating