Use the following to answer questions :
Scenario I
The scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Gilbertson,M.W. ,Shenton,M.E. ,Ciszewski,A. ,Kasai,K. ,Lasko,N .B. ,Orr,S.P. ,& Pitman,R.K.(2002) .Smaller hippocampal volume predicts pathologic vulnerability to psychological trauma.Nature Neuroscience,5,1242-1247.
Persons who live through a traumatic experience may develop posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) .PTSD is characterized by chronic physiological arousal,recurrent unwanted thoughts or images,and avoidance of things that bring the trauma to mind,with symptoms persisting for more than 1 month.Persons with PTSD also are at risk for other psychological disorders,with substance abuse disorder being a common comorbid diagnosis.In the last two decades,a number of studies have demonstrated that persons with PTSD have smaller hippocampi than controls.This may result from the neurotoxic effects of stress hormones examined the hippocampal volume of combat veterans with and without PTSD who each had an identical twin who never served in the military.Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.1.
Figure 15.1 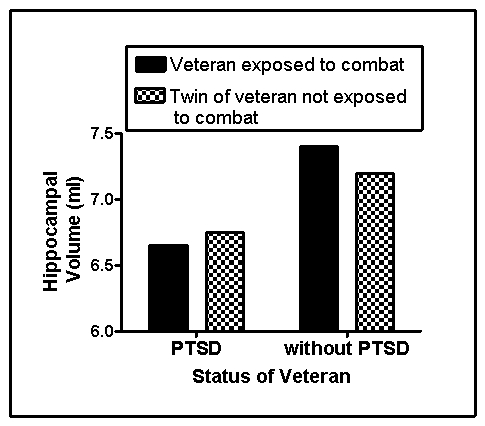
-(Scenario I) For a number of years,psychologists with expertise in the stress response hypothesized that glucocorticoid release at and shortly after the time of trauma was neurotoxic and led to smaller hippocampi.The results of the study by Gilbertson and colleagues (2002) :
Definitions:
Occipital Lobe
The portion of the cerebral cortex located at the back of the brain, responsible for processing visual information.
Cerebral Cortex
The surface of the cerebrum, the largest structure of the brain, which contains both sensory and motor nerve cell bodies.
Frontal
Frontal pertains to the front part of something, often referring to the frontal lobe of the brain which is associated with decision making, problem-solving, and controlling behavior.
Parietal
Pertaining to the parietal lobe of the brain, which is important for processing sensory information and spatial orientation.
Q37: Brain activation in response to threat occurs
Q71: Women who are involved in intense physical
Q85: In their research on the role of
Q108: Which disorder is NOT an anxiety disorder?<br>A)phobic
Q160: There is evidence that living at lower
Q167: The primary reason for the deinstitutionalization movement
Q216: Public health professionals have recognized for some
Q288: Double-blind assessments of treatment effectiveness are commonly
Q302: Threats,but not challenges,increase the constriction of blood
Q314: Even when participants are assigned to completely