Use the case below to answer the following question(s) .
The Tipton Hotel is considering a major remodeling effort and needs to determine the best combination of rates and suite sizes to maximize revenues.Currently,the hotel has 755 suites with the following history: 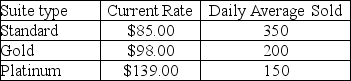 Each market segment has its own price/demand elasticity.Estimates are:
Each market segment has its own price/demand elasticity.Estimates are: 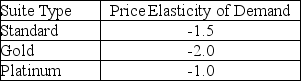 This means,for example,that a 1% decrease in the price of a standard suite will increase the number of suites sold by 1.5%.Similarly,a 1% increase in the price will decrease the number of suites sold by 1.5%.For any pricing structure (in $) ,the projected number of suites of a given type sold (we will allow continuous values for this problem) can be found using the formula:
This means,for example,that a 1% decrease in the price of a standard suite will increase the number of suites sold by 1.5%.Similarly,a 1% increase in the price will decrease the number of suites sold by 1.5%.For any pricing structure (in $) ,the projected number of suites of a given type sold (we will allow continuous values for this problem) can be found using the formula:
(Historical average number of suites sold) + (Elasticity) (New price - Current price) (Historical average number of suites sold) /(Current price)
The hotel owners want to keep the price of a standard suite between $70 and $90; a gold suite between $90 and $110; and a platinum suite between $120 and $149.
Define S = price of a standard suite,G = price of a gold suite,and P = price of a platinum suite.
-Using Solver,determine the projected number of standard suites sold.
Definitions:
Housing Price Index
A statistical measure designed to reflect the price changes of residential housing.
Case And Schiller
Researchers known for their work in analyzing home prices that led to the development of the S&P/Case-Shiller Home Price Indices.
Greenspan And Bernanke
Alan Greenspan and Ben Bernanke, both of whom served as Chairmen of the Federal Reserve, driving significant monetary policy decisions in the United States.
Socially Optimal Level
The socially optimal level refers to an outcome in production or activity where the social benefits are maximized and social costs minimized, often achieved through proper regulation or market mechanisms.
Q10: What is the probability of the drug
Q16: If you were to use a feminist
Q24: The production of a popular line of
Q24: How will the formula to calculate A16
Q36: For the given data set,the probability of
Q44: According to a feminist perspective,the jobs people
Q56: According to which theory would you argue
Q79: A typical charity raffle involves selling one
Q79: Using the above data,the number of overbooked
Q91: How does Solver create names in reports?