TABLE 15-4
The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test.She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing),daily mean of the percentage of students attending class (% Attendance),mean teacher salary in dollars (Salaries),and instructional spending per pupil in dollars (Spending)of 47 schools in the state.
Let Y = % Passing as the dependent variable,X1 = % Attendance,X2 = Salaries and X3 = Spending.
The coefficient of multiple determination (  )of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are,respectively,0.0338,0.4669,and 0.4743.
)of each of the 3 predictors with all the other remaining predictors are,respectively,0.0338,0.4669,and 0.4743.
The output from the best-subset regressions is given below: 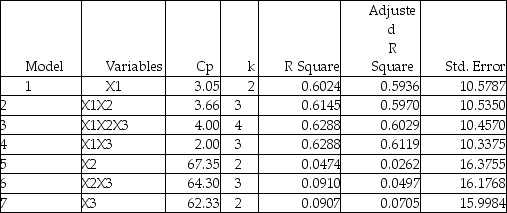 Following is the residual plot for % Attendance:
Following is the residual plot for % Attendance: 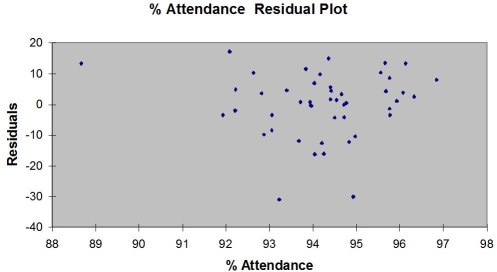 Following is the output of several multiple regression models:
Following is the output of several multiple regression models:
Model (I): 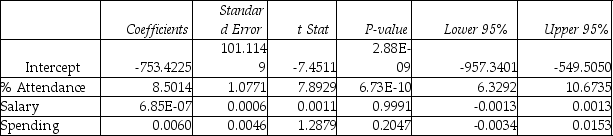 Model (II):
Model (II): 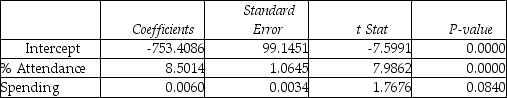 Model (III):
Model (III): 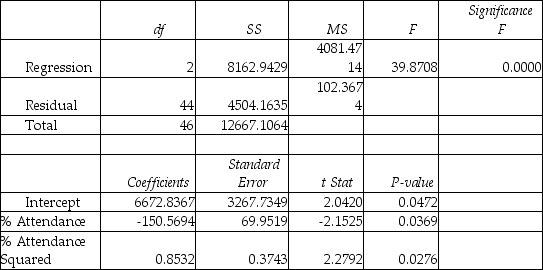
-True or False: Referring to Table 15-4,the quadratic effect of daily average of the percentage of students attending class on percentage of students passing the proficiency test is not significant at a 5% level of significance.
Definitions:
Partnership Debts
Debts that are the responsibility of the business partnership as a whole, not just of individual partners.
Duty to Account
An obligation to provide a detailed report of financial transactions or holdings.
Duty to Maintain
The obligation to keep property, equipment, or systems in good working condition through regular care, repair, and upkeep.
Implied Authority
The authority of an agent to perform acts which are reasonably necessary to accomplish the purpose of an organization.
Q23: An interaction term in a multiple regression
Q59: True or False: From the coefficient of
Q84: Referring to Table 13-4,the coefficient of correlation
Q101: Referring to Table 17-6,what is the experimental
Q113: Referring to Table 14-14,the fitted model for
Q130: True or False: Referring to Table 14-15,the
Q165: Referring to Table 13-9,the value of the
Q201: Referring to Table 13-4,the managers of the
Q267: Referring to Table 14-6,the coefficient of partial
Q269: Referring to Table 17-7,if one is already