TABLE 15-1
A certain type of rare gem serves as a status symbol for many of its owners. In theory, for low prices, the demand increases and it decreases as the price of the gem increases. However, experts hypothesize that when the gem is valued at very high prices, the demand increases with price due to the status owners believe they gain in obtaining the gem. Thus, the model proposed to best explain the demand for the gem by its price is the quadratic model:
Y = β₀ + β₁X + β₁X² + ε
where Y = demand (in thousands) and X = retail price per carat.
This model was fit to data collected for a sample of 12 rare gems of this type. A portion of the computer analysis obtained from Microsoft Excel is shown below: 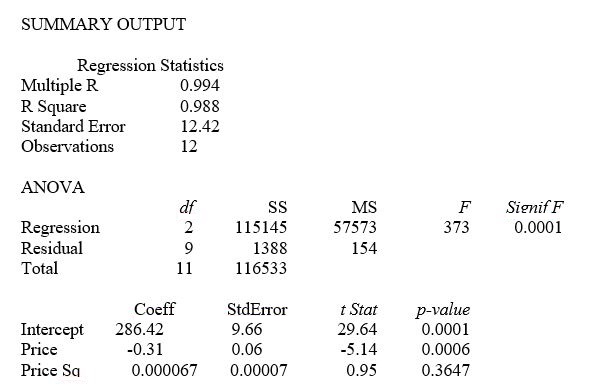
-Referring to Table 15-1, what is the p-value associated with the test statistic for testing whether there is an upward curvature in the response curve relating the demand (Y) and the price (X) ?
Definitions:
Fixed Expenses
Costs that do not vary with the volume of production or sales, such as rent, salaries, and insurance.
Contribution Margin
The difference between sales revenue and variable costs, indicating how much contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
Variable Expenses
Costs that change in proportion to the activity of a business, such as sales commissions or raw materials.
Net Operating Income
is the total profit of a company after operating expenses are subtracted from revenue but before deducting interest and taxes.
Q8: Referring to Table 15-5,what is the value
Q41: Referring to Table 16-5,exponentially smooth the number
Q56: True or False: In data mining where
Q66: Referring to Table 14-13,the effect of living
Q93: True or False: Referring to Table 14-18,there
Q97: Referring to Table 14-5,suppose the microeconomist wants
Q148: Referring to Table 17-10,Model 1,what are the
Q150: Referring to Table 16-9,if one decides to
Q189: Referring to Table 14-4,which of the following
Q291: Referring to Table 14-6,_% of the variation