TABLE 14-16
What are the factors that determine the acceleration time (in sec.) from 0 to 60 miles per hour of a car? Data on the following variables for 30 different vehicle models were collected:
Y (Accel Time) : Acceleration time in sec.
X1 (Engine Size) : c.c.
X2 (Sedan) : 1 if the vehicle model is a sedan and 0 otherwise
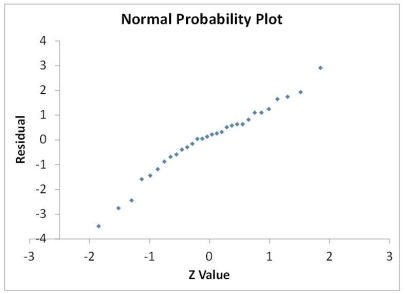
The regression results using acceleration time as the dependent variable and the remaining variables as the independent variables are presented below. 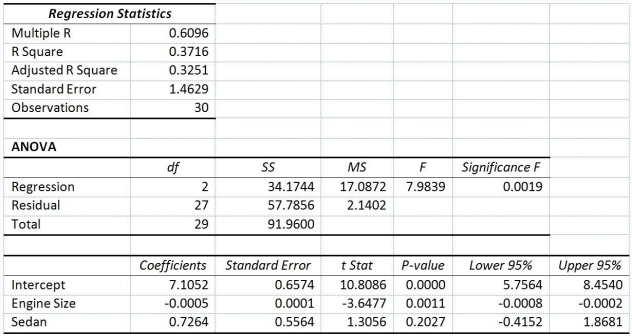 The various residual plots are as shown below.
The various residual plots are as shown below. 
 The coefficient of partial determinations
The coefficient of partial determinations 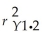 and
and 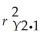 are 0.3301,and 0.0594,respectively.
are 0.3301,and 0.0594,respectively.
The coefficient of determination for the regression model using each of the 2 independent variables as the dependent variable and the other independent variable as independent variables ( 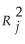 ) are,respectively 0.0077,and 0.0077.
) are,respectively 0.0077,and 0.0077.
-Referring to Table 14-16,what is the correct interpretation for the estimated coefficient for X1?
Definitions:
Punishment
A consequence that decreases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated, often used in the context of discipline or behavioral modification.
Reinforcer
Any stimulus that strengthens or increases the probability of a specific response or behavior by providing a consequence an individual finds rewarding.
Change Her Behavior
The process or act of modifying an individual's actions or reactions through various methods, such as reinforcement or punishment.
Conditioned Stimulus
A previously neutral stimulus that, after becoming associated with the unconditioned stimulus, eventually comes to trigger a conditioned response.
Q16: Referring to Table 16-16,what is the unweighted
Q35: Referring to Table 12-8,at 5% level of
Q52: Referring to Table 14-4,the coefficient of partial
Q61: Referring to Table 15-3,the prediction of time
Q77: True or False: A regression had the
Q102: Referring to Table 16-5,the number of arrivals
Q196: Referring to Table 13-3,the director of cooperative
Q212: Referring to Table 13-4,the managers of the
Q305: Referring to Table 14-7,the department head wants
Q330: Referring to Table 14-15,predict the percentage of