The logic rung shown is an example of a: 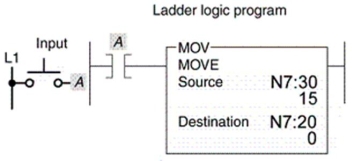
Definitions:
Procedural Unconscionability
A legal principle referring to circumstances where the process involved in making a contract is deemed unfair or unjust, often due to a significant imbalance in power or information between the parties.
Substantive Unconscionability
A legal doctrine that allows courts to refuse to enforce a contract or part of it, if the contract is excessively unfair or oppressive.
Adhesion Conscionability
A legal concept referring to the fairness of contract terms in a standard-form agreement, where one party has significantly more power to dictate the terms.
Exculpatory Clause
A statement in a contract that frees one party (usually the drafter of the agreement) from all liability arising out of performance of the contract, generally based on factors such as consumer ignorance or a great deal of unexplained fine print that serve to deprive the less powerful party of a meaningful choice.
Q11: Assume output SOL C is energized at
Q12: The basic rule for an XOR function
Q19: For the 24-hour clock program,Counter C5:1 is
Q28: For the program shown,instruction B represents an:
Q34: Assume the value stored in N7:0 is
Q40: The symbol shown is that for a:
Q45: The Output Energize instruction:<br>A)is also known as
Q57: A controller scope tag consists of data
Q72: The programming device monitor normally indicates a
Q74: Nested subroutines make complex programming easier.