Maintenance Company for a Maintenance Company,a Payoff Table,the Prior Probabilities for Probabilities
Maintenance Company
For a maintenance company,a payoff table,the prior probabilities for three states of nature,and the likelihood probabilities are shown below:
Payoff Table:  Prior Probabilities: P(s1)= 0.4,P(s2)= 0.5,and P(s3)= 0.1. Likelihood Probabilities:
Prior Probabilities: P(s1)= 0.4,P(s2)= 0.5,and P(s3)= 0.1. Likelihood Probabilities: 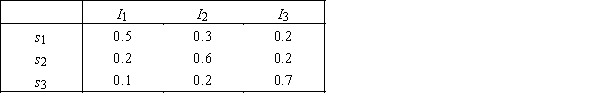
-{Maintenance Company Narrative} Use the posterior probabilities for I2 in the previous question to recalculate the expected monetary value of each act,then determine the optimal act and the EMV*.
Definitions:
Standard Deviation
Standard Deviation measures the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values, indicating how much the values in a dataset deviate from the mean.
Heights
The measurement of someone or something from base to top or head to foot.
Statistically Significant
An indication that the likelihood of the observed data, under the assumption of the null hypothesis, is low enough to reject the null hypothesis.
Electronic Control
The use of electronic systems to regulate the operation of mechanical devices, commonly found in automotive, industrial, and consumer appliance contexts.
Q3: _ techniques allow us to make estimates
Q4: Comparing the output of strawberries grown on
Q6: A hypothesis test is used to determine
Q7: Which of the following would be considered
Q22: Prior to 1950,African American men had the
Q31: Nonparametric procedures are often called _-free statistics.
Q97: {The Pyramids of Giza Narrative} Plot the
Q100: To determine whether the process distribution standard
Q103: Discuss what we mean by chance variation
Q156: The Kruskal-Wallis test can be conducted as