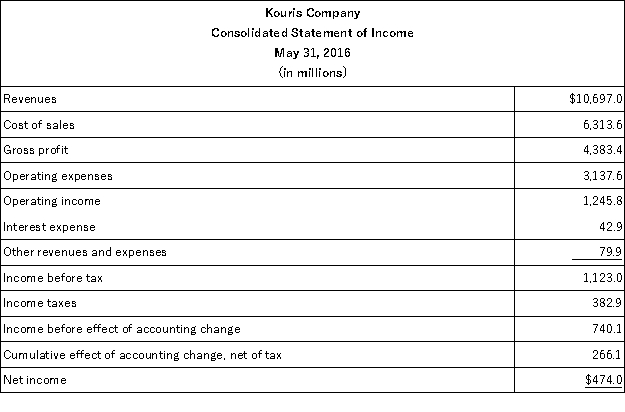
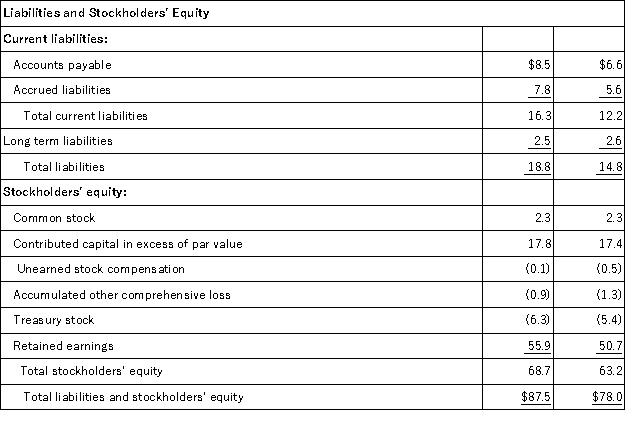
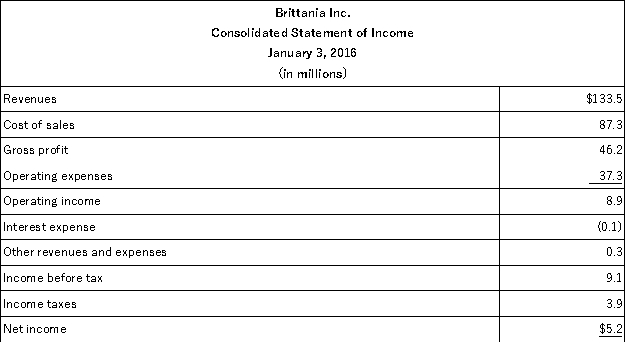
The following summaries from the income statements and balance sheets of Kouris Company and Brittania,Inc.are presented below.
(1)For both companies for 2016,compute the:
(a)Current ratio
(b)Acid-test ratio
(c)Accounts receivable turnover
(d)Inventory turnover
(e)Days' sales in inventory
(f)Days' sales uncollected
Which company do you consider to be the better short-term credit risk? Explain.
(2)For both companies for 2016,compute the:
(a)Profit margin ratio
(b)Return on total assets
(c)Return on common stockholders' equity
Which company do you consider to have better profitability ratios? 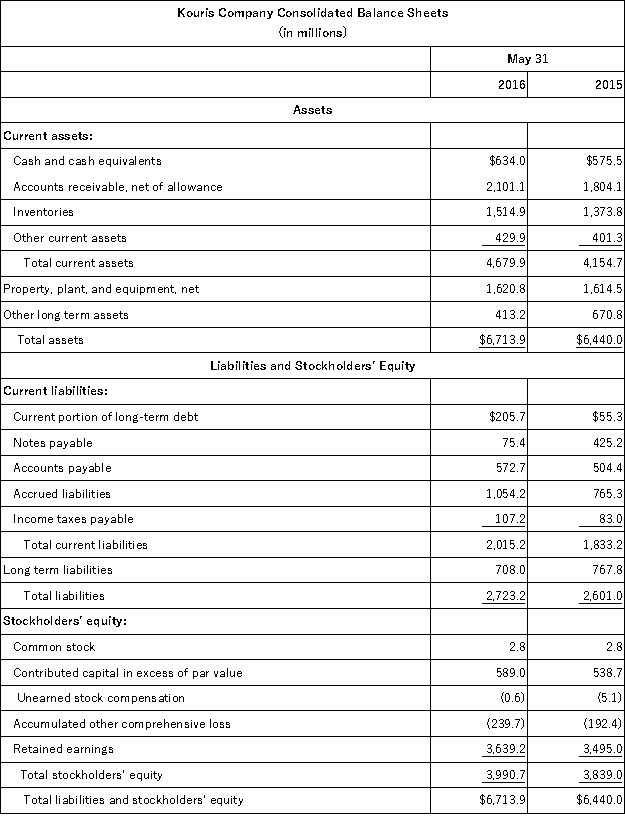

Definitions:
Perfect Competitor
An individual or company within a perfectly competitive market that cannot influence the market price and must accept the prevailing market price.
Long Run
In economics, a period in which all inputs and outputs can be varied, allowing for the adjustment of all factors of production.
Perfect Competitor
A theoretical market where no individual buyer or seller has the power to affect the price of goods, leading to an optimal allocation of resources.
Long Run
A period in economics sufficient for all markets to adjust, including prices, outputs, and wages, reflecting changes in economic conditions or policies.
Q7: Just-in-time manufacturing is a system that acquires
Q21: A company had net cash flows from
Q55: Information for the Deuce Manufacturing Company follows.Compute
Q70: Using the information below,compute the Days' sales
Q140: A company had net income of $86,000
Q149: _ activities generally include those transactions and
Q156: _ financial statements show the financial position,results
Q158: Refer to the following selected financial information
Q161: Manufacturing costs other than direct materials and
Q170: Long-term investments include investments in land or