Horizontal Merger
The following questions refer to the accompanying diagram, which shows the effects of a horizontal merger. Before the merger, the firm behaves competitively producing Q0 and charging P0. The merger lowers the firm's marginal cost and gives the firm enough market power to switch to the monopoly equilibrium.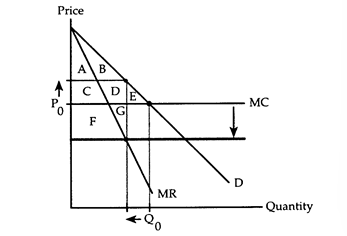
-Refer to Horizontal Merger.As a consequence of the merger,consumers lose surplus equal to
Definitions:
Par Value
The face value of a bond or stock as stated by the issuer, which has implications for interest calculations or dividends.
Yield to Maturity
Yield to Maturity (YTM) is the total return anticipated on a bond if the bond is held until it matures, considering all payments from now until maturity, including coupon payments and the difference between the purchase price and the par value.
Coupon Rate
The annual interest rate paid on a bond, expressed as a percentage of the face value, to the bondholders.
Face Value
Face value is the nominal value stated on a financial instrument such as a bond or a stock certificate, important in determining its maturity value or dividend payments.
Q2: Derived demand for an input is the
Q19: Refer to Sales Tax.After the tax is
Q28: Which of the following will result in
Q45: Refer to the market diagram.Relative to the
Q50: A player has a dominant strategy when
Q52: In order to maximize profits,firms should produce
Q53: An increase in the marginal productivity of
Q62: Suppose the government spends $5,000 per person
Q66: One problem with a Clarke tax is
Q71: Refer to Horizontal Merger.The result of the