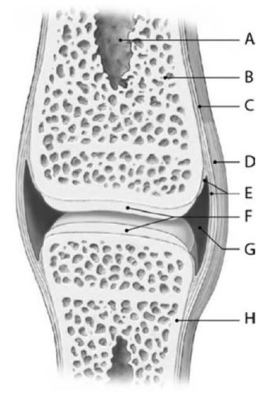
 Figure 6-4 Synovial Joint (Sagittal Section)
Figure 6-4 Synovial Joint (Sagittal Section)
Use Figure 6-4 to identify the labeled part.
-Which joint type can perform rotation movements?
Definitions:
Sagittal Suture
A fibrous joint that connects the two parietal bones of the skull along the midline, resembling a seam, contributing to the skull's rigidity and shape.
Synovial Fluid
A viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints, serving to reduce friction between the articular cartilages during movement.
Range of Motion
The complete range of motion available in a joint, encompassing both flexion and extension capabilities.
Torn Ligament
A stretch or tear of a ligament, the fibrous tissue connecting bones and joints, often caused by sudden twists or excessive force.
Q16: _ cells connect photoreceptors to ganglion cells.<br>A)
Q23: Merocrine sweat glands<br>A) are most common in
Q44: Which of the following constitutes most of
Q50: In simple inheritance,<br>A) phenotypic characteristics are determined
Q77: The sensory nuclei of cranial nerves V-VIII
Q78: The daily day/night cycle known as a
Q82: Briefly explain the process of active transport
Q87: Night blindness can be treated by administering<br>A)
Q146: The _ establishes emotional states.<br>A) basal nuclei<br>B)
Q166: Mary has just finished pitching a fast-pitch