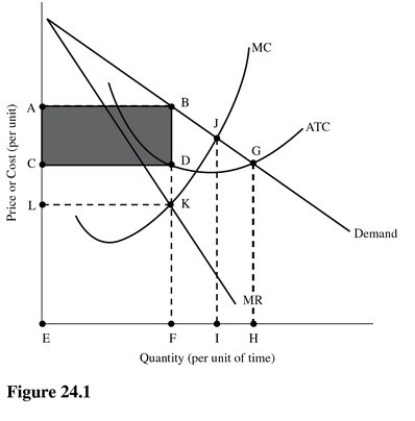
 In Figure 24.1,total revenue is represented by the area
In Figure 24.1,total revenue is represented by the area
Definitions:
Additional Costs
Expenses that are not initially accounted for in the budget or pricing but arise during the execution of a project or the production of goods.
Marginal Analysis
Marginal analysis refers to the examination of the benefits and costs of a small (marginal) change in the production, consumption, or allocation of resources.
Ceteris Paribus
A principle in economics that states other conditions remain constant while one variable changes.
Marginal Benefit
The additional satisfaction or value gained from consuming or producing one more unit of a good or service.
Q9: Table 21.2 <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\begin{array}{|l|r|r|r|r|}\hline
Q26: Sellers in a perfectly competitive market are
Q30: For perfectly competitive firms,price<br>A)Is greater than marginal
Q51: A monopoly is a market in which
Q95: Perfect competition is a situation in which<br>A)Every
Q100: Economic losses mean that firms will exit
Q126: In industries where government regulates price,individual firms
Q126: Table 25.2 <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\begin{array}
Q127: Economic profit is<br>A)Greater than accounting profit by
Q147: In a perfectly competitive market,firms will earn