The table below shows various values of labour (L) ,capital (K) ,and technology (T) for Economies A,B,and C.In each case,the aggregate production function takes the following form: Y = T × 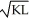
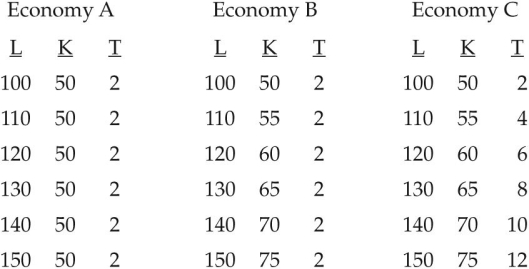 TABLE 25-4 Refer to Table 25-4.The production function that applies to Economies A,B,and C displays
TABLE 25-4 Refer to Table 25-4.The production function that applies to Economies A,B,and C displays
Definitions:
Self-Incompatibility
A mechanism in plants that prevents self-fertilization and encourages cross-pollination by rejecting pollen from the same or genetically similar individuals.
Hermaphroditic
Describes an organism that possesses both male and female reproductive organs, allowing it to perform both roles in reproduction.
Allele Frequency
The proportion of all copies of a particular gene in a population that are of a given allele type, influencing genetic diversity and evolution.
Hardy-Weinberg Theorem
A principle that states allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences.
Q10: Which one of the following statements best
Q32: Consider the following news headline: "Information technology
Q51: Northern Bank: Balance Sheet Assets Liabilities<br>Reserves $800
Q67: Loans from the Bank of Canada are<br>A)made
Q90: Consider the long-run theory of investment,saving and
Q95: In 1950,when the world's population was 2.5
Q103: Suppose the Bank of Canada chooses to
Q107: Other things being equal,an economy with a
Q116: Consider the following table for a hypothetical
Q123: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7713/.jpg" alt=" FIGURE 27-5 Refer