What kind of reaction does the conversion of A to D represent? 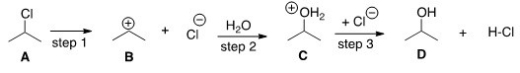
Definitions:
Chiral Center
A carbon atom that is attached to four different groups, making its mirror images non-superimposable.
Stereoisomer
Molecules that have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space.
Configuration
The fixed arrangement of atoms in a molecule that cannot be changed without breaking chemical bonds, different from conformation.
Asymmetric Carbon
A carbon atom bonded to four different groups or atoms, leading to chirality and optical activity in molecules.
Q8: Identify the Lewis base in the following
Q8: Determine the product of the following reaction.
Q12: Rearrangements can occur in which of the
Q34: Which of the following best describes the
Q43: Give the IUPAC name for the following
Q45: Which of the following statements about the
Q48: Which of the following statements about the
Q48: What is the major product of the
Q57: What is the starting material in the
Q58: Which is the correct Lewis structure for