Fundamental Value Based on Absolute PPP. Ideally, one would like to compare directly the price
of goods in two countries to see if an exchange rate conforms to absolute PPP, or whether it is overvalued or undervalued in real terms. As mentioned in Chapter 2, this can only be done for some individual goods that are clearly comparable ("law of one price"), and the estimation for different goods can lead to opposing conclusions. In Chapter 2, we provide an analysis based on the well-known Big Mac report of The Economist. Of course, the Big Mac is a very particular product and a fundamental PPP value can be computed on a wide range of products. The results are often conflicting. For example, one can look at production prices rather than consumption prices. Some studies are conducted by looking at labor costs. Rather than looking at unit labor costs for unskilled workers, as is often done, the exhibit below reports the average annual remuneration of the chief executive officer (CEO) of industrial companies with annual revenues of $250 million to $500 million in ten selected areas of the world. The figures are also from April 1998. They include all forms of compensation, such as bonuses, perks, and stock options, but are not adjusted for different taxes or costs of living.
The first column gives the total CEO compensation measured in U.S. dollars using the actual exchange rate, which is indicated in the second column. The third column gives the fundamental PPP value of each currency, implied by the national CEO compensations. It is the exchange rate with the dollar that would make CEO compensation identical in all countries. The fourth column gives the actual overvaluation (if positive) or undervaluation (if negative) of the local currency relative to its fundamental value in terms of CEO compensation.
EXHIBIT: Determining a Fundamental PPP Value Based on CEOs' Remuneration
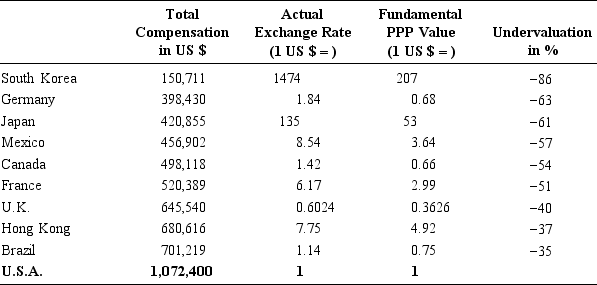 Source: Total compensation data comes from Towers Perrin, 1998.
Source: Total compensation data comes from Towers Perrin, 1998.
What conclusions can you draw from this exhibit?
Definitions:
Binomial Model
A financial model used to price options by considering two potential outcomes (up or down) over time for the underlying asset.
Option Valuation
The process of determining the fair market value of options using various models, taking into account factors like the underlying asset, time to expiration, and volatility.
Black-Scholes Model
A mathematical model used to price European-style options, identifying the theoretical fair price for puts and calls based on time and other risk factors.
Time Value
The additional amount of money an investor is willing to pay for an option or bond, above its intrinsic value, due to the time left until expiration.
Q5: Which removes mucus?<br>A) Coughing<br>B) Deep breathing<br>C) Incentive
Q14: In the early 1990s, France and Germany
Q30: Respirations gradually increase in rate and depth
Q39: Which health team member decides how much
Q41: You hold a portfolio made of
Q46: Individuals with AIDS or HIV are "disabled"
Q46: Post-traumatic stress syndrome occurs<br>A) After a terrifying
Q53: A resident has AD. She tends to
Q86: XLT Corp. is pursuing a cooperative strategy
Q144: A patient has cancer. You find the