Determine the standard enthalpy of formation of Fe2O3(s) given the thermochemical equations below. Fe(s) + 3 H2O( 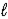 ) → Fe(OH) 3(s) + 3/2 H2(g)
) → Fe(OH) 3(s) + 3/2 H2(g)
ΔrH° = +160.9 kJ/mol-rxn
H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) → H2O( 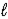 )
)
ΔrH° = -285.8 kJ/mol-rxn
Fe2O3(s) + 3 H2O( 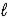 ) → 2 Fe(OH) 3(s)
) → 2 Fe(OH) 3(s)
ΔrH° = +288.6 kJ/mol-rxn
Definitions:
Optical Illusion
Visual perceptions that differ from objective reality, often involving misleading or distorted images that the brain interprets in a manner that diverges from the physical measurement of the stimulus source.
Optical Illusion
A visual phenomenon where what we perceive differs from objective reality, often due to the brain's interpretation of visual information.
Bending Light Rays
The refraction of light that occurs when its speed changes as it passes from one medium to another, causing the light to change direction.
Fatigue
A state of physical or mental weariness resulting from exertion, reducing efficiency and capacity for work.
Q2: According to VSEPR theory,which of the following
Q5: When a user enters his username and
Q19: Which type of experiment demonstrates that light
Q20: Which of the following molecules or ions
Q34: Express the result of the following calculation
Q43: What 2- ion has the following ground
Q44: To form a molecule with a tetrahedral
Q55: A mixture of KCl and KClO<sub>3</sub> weighing
Q71: Pure copper may be produced by the
Q93: Which of the following is the common