Determine the standard enthalpy of formation of Fe2O3(s) given the thermochemical equations below. Fe(s) + 3 H2O( 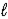 ) → Fe(OH) 3(s) + 3/2 H2(g)
) → Fe(OH) 3(s) + 3/2 H2(g)
ΔrH° = +160.9 kJ/mol-rxn
H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) → H2O( 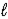 )
)
ΔrH° = -285.8 kJ/mol-rxn
Fe2O3(s) + 3 H2O( 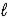 ) → 2 Fe(OH) 3(s)
) → 2 Fe(OH) 3(s)
ΔrH° = +288.6 kJ/mol-rxn
Definitions:
Sample Size
The number of observations or data points collected in a sample from a population for the purpose of statistical analysis.
Confidence Interval
A range of values, derived from sample data, that likely contain the population parameter with a certain level of confidence.
Level of Confidence
The degree of certainty or probability that the results of statistical analysis are reliable and not due to random chance.
Confidence Interval
A range of values derived from sample data that is likely to contain the value of an unknown population parameter, expressed at a given level of confidence.
Q19: A flexible vessel contains 53 L of
Q26: For which of the following molecules does
Q28: C<sub>2</sub>H<sub>2</sub>F<sub>4</sub> is the formula for two possible
Q29: What volume of 1.27 M HCl is
Q35: Which of the following is the largest
Q42: An event log entry that is an
Q49: Which feature on an NTFS volume provides
Q68: When a water molecule forms a hydrogen
Q75: A 5.95-g sample of AgNO<sub>3</sub> is reacted
Q88: Sodium azide decomposes rapidly to produce nitrogen