Use the following information when answering the corresponding questions) .
Suzanne Simard and colleagues knew that the same mycorrhizal fungal species could colonize multiple types of trees. They w if the same fungal individual would colonize different trees, forming an underground network that potentially could transpor and nutrients from one tree to another S. Simard et al. 1997. Net transfer of carbon between mycorrhizal tree species in the fi Nature 388:579- 82) . Figure 29.2 illustrates the team's experimental setup. Pots containing seedlings of three different tree species were set up and grown under natural conditions for three years; two of the three species formed ectomycorrhizae Douglas fir, birch) and the other cedar) formed arbuscular mycorrhizae. For the experiment, the researchers placed airtight bags over the Douglas fir and birch seedlings; into each bag, they injected either carbon dioxide made from carbon- 13 or carbon- 14 13CO2 and 14CO2, isotopes of carbon) . As the seedlings photosynthesized, the radioactive carbon dioxide was converted into radioactively labelled sugars that could be tracked and measured by the researchers.
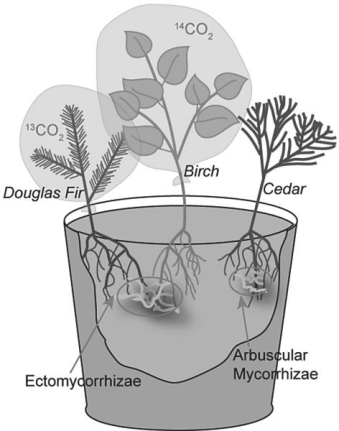 Figure 29.2
Figure 29.2
-Referring to Simard et al. 1997) , what is the result that would most strongly refute their hypothesis?
Definitions:
Civil Rights Act
Legislation in various countries aimed at prohibiting discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin, and promoting equality.
Verbal Offenses
Verbal offenses involve using words to insult, belittle, or speak harmful untruths about someone, which can lead to emotional hurt and conflict.
Instructional Method
Techniques, strategies, and approaches used by educators to facilitate learning.
Traditional Classroom Programs
Educational courses or curriculums delivered in a conventional classroom setting, characterized by face-to-face interaction between students and instructors.
Q1: What two major novelties allowed for the
Q5: Regulatory transcription factors<br>A) influence the assembly of
Q7: Which of the following is an example
Q10: Researchers are interested in improving crop plants
Q10: In the pressure- flow mechanism, loading of
Q33: Why can gene expression be altered more
Q36: The difference between a polar covalent bond
Q40: Why doesn't inbreeding depression, by itself, cause
Q48: Wikelski and Romero 2003) found that large
Q55: When tobacco plants were exposed to far-