Use the graphs in Figures 29.4 and 29.5 and the following information when answering the corresponding questions.
Canadian and Swiss researchers van der Heijden et al., 1998) interested in factors affecting biodiversity, grew a variety of gra plants in combination with one of four arbuscular mycorrhizal AMF) species, no AMF, or all four AMF species together; and measured plant growth under each set of conditions. All plant species were grown in each plot, so they always competed with each other with the only difference being which AMF were present. Use the graphs in Figure 31.5 to answer the questions
that follow. Note that the x- axis labels indicate the number and identity of AMF species bar 0 = no fungi; bars A- D = individual AMF species; bar A+B+C+D = all AMF species together) . The y- axis indicates the amount grams) of plant biomass for the species shown in italics above each graph. Graph e) is the total biomass grams) of all 11 plant species combined; graph f) is the biomass of Bromus erectus plants only, separated from the total.
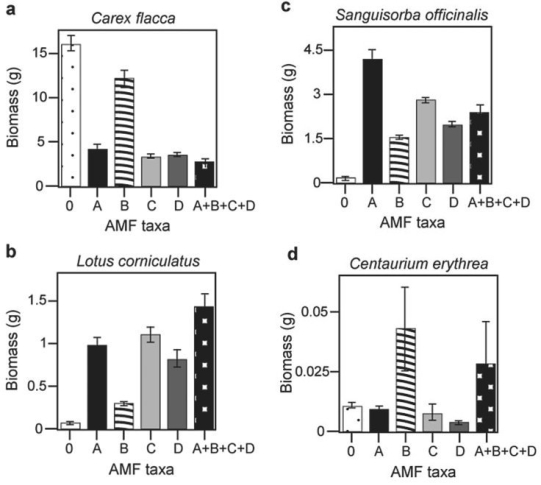 Figure 29.4
Figure 29.4
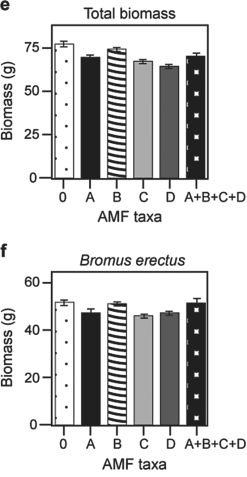 Figure 29.5
Figure 29.5
-What is the major difference between Bromus erectus graph f) and the other plant species graphs a- d) included in the study?
Definitions:
Persuasive Authorities
Legal sources that can influence a decision but are not binding on the court, such as cases from other jurisdictions or legal treatises.
Binding
Having legal force or effect; obligating parties to comply with the terms set forth in a contract or agreement.
Courts
The governmental institutions authorized to settle disputes between parties in legal matters.
Persuasive Authorities
Sources of law, such as cases or statutes from other jurisdictions, that a court may consider for guidance but are not binding.
Q1: Which of the following is a reason
Q2: Why did the researchers wear protective clothing
Q2: Who proposed that organisms could be organized
Q9: Plasmids are used as cloning vectors in
Q10: Which of the following events would be
Q11: Which of the following observations about flagella
Q20: Which of these are spore- producing structures?<br>A)
Q24: Imagine that you are searching for the
Q32: During chemical evolution, which of the following
Q35: In combination, what do the products of