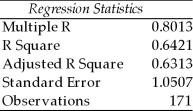
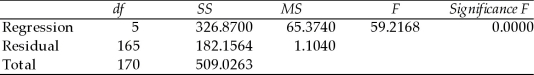
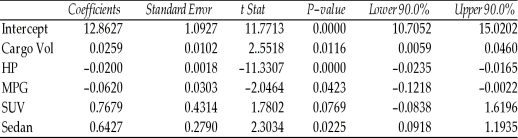
TABLE 15-5
What are the factors that determine the acceleration time (in sec.) from 0 to 60 miles per hour of a car? Data on the following variables for 171 different vehicle models were collected:
Accel Time: Acceleration time in sec.
Cargo Vol: Cargo volume in cu. ft.
HP: Horsepower
MPG: Miles per gallon
SUV: 1 if the vehicle model is an SUV with Coupe as the base when SUV and Sedan are both 0
Sedan: 1 if the vehicle model is a sedan with Coupe as the base when SUV and Sedan are both 0
The regression results using acceleration time as the dependent variable and the remaining variables as the independent variables are presented below.
 ANOVA
ANOVA
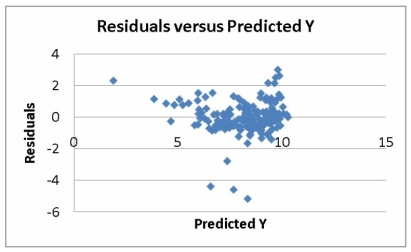
 The various residual plots are as shown below.
The various residual plots are as shown below.
 The coefficient of partial determination (
The coefficient of partial determination ( 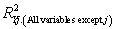 ) of each of the 5 predictors are, respectively, 0.0380, 0.4376, 0.0248, 0.0188, and 0.0312.
) of each of the 5 predictors are, respectively, 0.0380, 0.4376, 0.0248, 0.0188, and 0.0312.
The coefficient of multiple determination for the regression model using each of the 5 variables as the dependent variable and all other X variables as independent variables ( 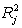 ) are, respectively, 0.7461, 0.5676, 0.6764, 0.8582, 0.6632.
) are, respectively, 0.7461, 0.5676, 0.6764, 0.8582, 0.6632.
-Referring to Table 15-5, what is the correct interpretation for the estimated coefficient for MPG?
Definitions:
Genetically Engineered
Organisms that have had their genetic material altered in a way that does not occur naturally through mating and/or natural recombination.
E. Coli
Escherichia coli, a commonly occurring bacterium in the intestines of warm-blooded organisms, some strains of which can cause food poisoning.
Dideoxynucleotides
Modified nucleotides used in DNA sequencing methods to terminate DNA strand elongation due to the absence of a 3' hydroxyl group.
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the exact sequence of nucleotides within a DNA molecule, vital for genetic research and forensic analysis.
Q15: In the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis,
Q35: Referring to Table 12-4, of the cell
Q43: Referring to Table 16-5, in testing the
Q75: The interpretation of the slope is different
Q85: Referring to Table 14-15, we can conclude
Q101: Referring to Table 17-1, what is the
Q127: The R chart is a control chart
Q144: Referring to Table 12-4, find the rejection
Q152: Referring to Table 12-6, the same decision
Q156: Referring to Table 14-3, the p-value for