TABLE 15-1
A certain type of rare gem serves as a status symbol for many of its owners. In theory, for low prices, the demand increases and it decreases as the price of the gem increases. However, experts hypothesize that when the gem is valued at very high prices, the demand increases with price due to the status owners believe they gain in obtaining the gem. Thus, the model proposed to best explain the demand for the gem by its price is the quadratic model:
Y = β₀ + β₁X + β₁X² + ε
where Y = demand (in thousands) and X = retail price per carat.
This model was fit to data collected for a sample of 12 rare gems of this type. A portion of the computer analysis obtained from Microsoft Excel is shown below: 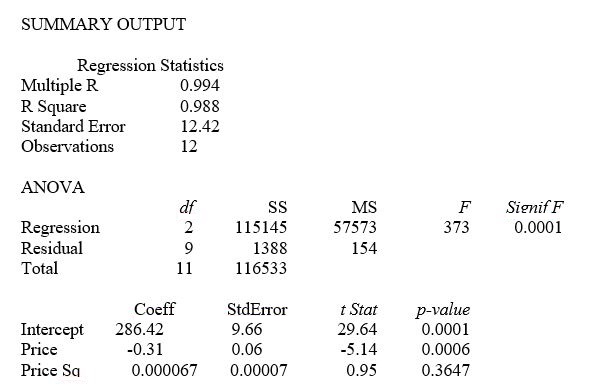
-Referring to Table 15-1, a more parsimonious simple linear model is likely to be statistically superior to the fitted curvilinear for predicting sale price (Y).
Definitions:
Objectives
Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals set by an organization or individual to guide actions and measure performance.
Money
A medium of exchange in the form of coins and banknotes; used to facilitate transactions for goods and services.
Paired Comparison Method
A technique used in performance appraisal where employees are evaluated by comparing them with each other in pairs.
Performance Appraisal
An ongoing process whereby an employer evaluates an employee's job performance and productivity in relation to pre-established criteria and organizational objectives.
Q19: Referring to Table 17-9, an R chart
Q30: Referring to Table 14-15, we can conclude
Q39: Referring to Table 15-5, what is the
Q46: Changes in the system to reduce common
Q58: Referring to Table 15-5, which of the
Q60: The coefficient of multiple determination r<sup>2</sup><sub>Y</sub><sub>.12</sub> measures
Q92: Referring to Table 17-9, an R chart
Q97: Referring to Table 17-7, based on the
Q121: The confidence interval for the mean of
Q149: Referring to Table 14-11, what null hypothesis