TABLE 14-15
The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test. She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing), daily average of the percentage of students attending class (% Attendance), average teacher salary in dollars (Salaries), and instructional spending per pupil in dollars (Spending) of 47 schools in the state.
Following is the multiple regression output with Y = % Passing as the dependent variable, X1= % Attendance, X2= Salaries and X3= Spending:
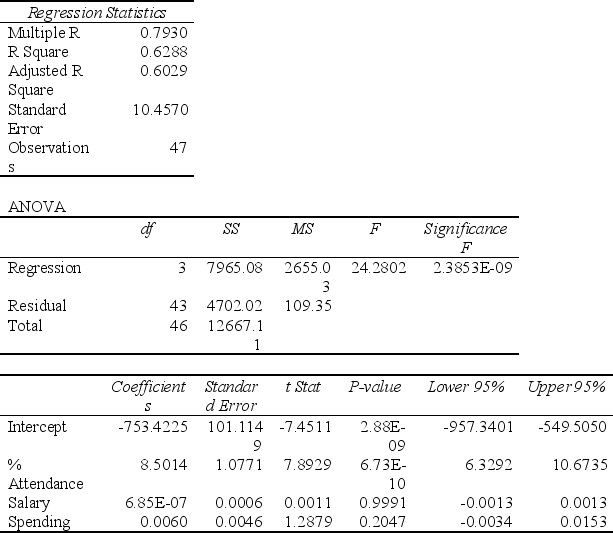 Note:
Note:
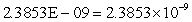
-Referring to Table 14-15, predict the percentage of students passing the proficiency test for a school which has a daily average of 95% of students attending class, an average teacher salary of 40,000 dollars, and an instructional spending per pupil of 2000 dollars.
Definitions:
Test Statistic
A value derived from sample data used in hypothesis testing to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis.
Null Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis that assumes no significant difference or effect exists between specified populations or parameters.
Alternative Hypothesis
A hypothesis that contradicts the null hypothesis by stating there is a statistically significant effect or relationship between variables.
Null Hypothesis
A default hypothesis that there is no significant difference or effect, used as a starting point for statistical hypothesis testing.
Q4: If a time series does not exhibit
Q31: Referring to Table 13-3, the regression sum
Q42: Referring to Table 17-9, construct an <img
Q69: Referring to Table 14-4, suppose the builder
Q80: Referring to Table 17-10, a c chart
Q126: Common causes of variation are correctable without
Q131: Referring to Table 14-15, what is the
Q134: If the sample sizes in each group
Q159: Referring to Table 14-3, the p-value for
Q171: Referring to Table 13-10, construct a 95%