TABLE 13- 11
A company that has the distribution rights to home video sales of previously released movies would like to use the box office gross (in millions of dollars) to estimate the number of units (in thousands of units) that it can expect to sell. Following is the output from a simple linear regression along with the residual plot and normal probability plot obtained from a data set of 30 different movie titles:
ANOVA
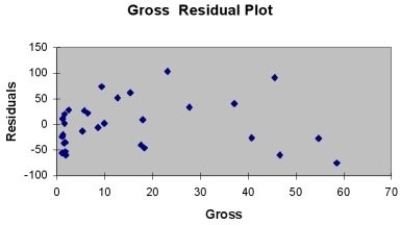
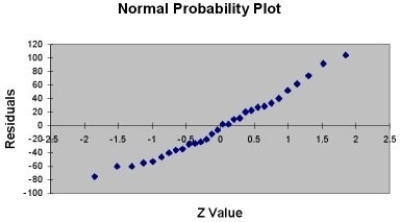
-Referring to Table 13-11, what are, respectively, the lower and upper limits of the 95% confidence interval estimate for population slope?
Definitions:
Beliefs And Values
These are fundamental principles or ideas that an individual or group holds to be true and important, guiding their behavior and decision-making.
Disciplined Focus
A methodical approach to maintaining attention and effort on set goals and tasks.
Zaleznik's Typology
A classification system devised by Abraham Zaleznik that differentiates leaders from managers based on their psychological motivations and patterns of behavior.
Kelley's Approach
A method outlined by Robert Kelley, focusing on the distinctions between followers and how they can become more effective in their roles.
Q13: Referring to Table 15-5, the 0 to
Q29: Referring to Table 13-5, the partner wants
Q59: If the sample sizes in each group
Q68: Collinearity is present if the dependent variable
Q78: The _ (larger/smaller) the value of the
Q117: Referring to Table 13-8, what are the
Q148: Referring to Table 12-12, which of the
Q157: Referring to Table 12-17, the critical value
Q176: Referring to Table 10-6, if we were
Q183: Referring to Table 14-2, for these data,