The fluorocarbon 
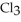
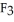 has a normal boiling point of 47.6 °C. The specific heats of
has a normal boiling point of 47.6 °C. The specific heats of 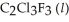 and
and 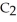
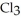
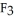 (g) are 0.91 J g-1 °C-1 and 0.67 J g-1 °C-1, respectively. The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ mol-1. The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at
(g) are 0.91 J g-1 °C-1 and 0.67 J g-1 °C-1, respectively. The heat of vaporization of the compound is 27.49 kJ mol-1. The heat required to convert 50.0 g of the compound from the liquid at 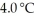 to the gas at 70.0 °C is ________ kJ.
to the gas at 70.0 °C is ________ kJ.
Definitions:
Alzheimer's Disease
A progressive neurodegenerative disorder that causes memory loss, cognitive decline, and ultimately, loss of ability to carry out simple tasks.
Neurological Disorder
Any condition that is caused by a dysfunction in part of the brain or nervous system, leading to physical and/or psychological symptoms.
Korsakoff's Syndrome
A chronic memory disorder caused by severe deficiency of thiamine (vitamin B1), most commonly associated with prolonged alcoholism.
Chronic Alcoholism
A severe form of alcohol dependency characterized by prolonged excessive drinking, leading to significant physical, social, and mental health issues.
Q20: A molecule or ion with five electrons
Q29: Identify the strongest bond.<br>A) single covalent bond<br>B)
Q33: Use the data given below to construct
Q54: Of the following, which element has the
Q75: Using the periodic table, identify the element
Q94: Determine the molecular geometry for the molecule
Q103: Which of the following statements is TRUE?<br>A)
Q126: Draw the Lewis structure for SF<sub>6</sub>. What
Q129: The rate of disappearance of HBr in
Q137: Calculate the osmotic pressure, in bar, of