Use the standard reaction enthalpies given below to determine 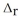 H° for the following reaction: P4(g) + 10Cl2(g) → 4PCl5(s)
H° for the following reaction: P4(g) + 10Cl2(g) → 4PCl5(s) 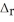 H° = ?
H° = ?
Given:
PCl5(s) → PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) 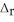 H°= +157 kJ
H°= +157 kJ
P4(g) + 6Cl2(g) → 4PCl3(g) 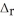 H° = -1207 kJ
H° = -1207 kJ
Definitions:
Romantic Love
A deep emotional and physical attraction to another person, often characterized by passion, intimacy, and commitment.
Sexual Orientation
A person's pattern of emotional, romantic, or sexual attraction to others, often categorized based on the gender relation to the individual.
Heterosexual
Referring to a person who is sexually attracted to members of the opposite sex.
Same-Gender Friendships
Friendships where both individuals identify as the same gender, providing a unique social support system.
Q14: Which of the following statements is TRUE?<br>A)
Q20: A FeCl<sub>3</sub> solution is 0.175 mol L<sup>-1</sup>.
Q27: Calculate the orbital for the hydrogen atom
Q41: Which of the gases in the graph
Q54: How many H<sup>+</sup> ions can the acid
Q63: The p orbital can hold a maximum
Q82: How many millilitres of ozone gas at
Q118: The attraction and repulsion between chanrged particles
Q121: Each of the following sets of quantum
Q140: Which of the following signs on q