Sorice Corporation uses activity-based costing to assign overhead costs to products. Overhead costs have already been allocated to the company's three activity cost pools as follows: Processing, $20,200; Supervising, $11,000; and Other, $66,800. Processing costs are assigned to products using machine-hours (MHs) and Supervising costs are assigned to products using the number of batches. The costs in the Other activity cost pool are not assigned to products. Activity data appear below: 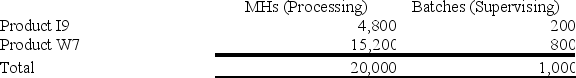 The activity rate for the Supervising activity cost pool under activity-based costing is closest to:
The activity rate for the Supervising activity cost pool under activity-based costing is closest to:
Definitions:
Throughput
The time required to move orders through the production process, from receipt to delivery.
Rated Capacity
The maximum amount of output that a system, facility, or machine is designed to produce under specified conditions.
Expected Output
The anticipated quantity or result produced by a process or system within a certain period.
Fixed Costs
Costs that do not change with the level of output or sales, such as rent, salaries, and insurance premiums, over a specified period.
Q1: A cost that will be incurred regardless
Q28: Boudoin Corporation manufactures two products: Product T72T
Q51: (Ignore income taxes in this problem.) The
Q84: Tustin Corporation has provided the following data
Q94: The simple rate of return is computed
Q105: In a sell or process further decision,
Q181: Cybil Baunt just inherited a 1958 Chevy
Q202: An activity-based costing system that is designed
Q235: Absorption costing treats all fixed costs as
Q250: Harootunian Corporation uses a job-order costing system