Roads are often designed with parabolic surfaces to allow rain to drain off.A particular road that is 44 feet wide is 0.4 foot higher in the center than it is on the sides (see figure) . 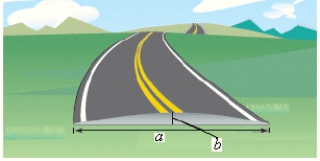
Where 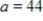 ft,
ft, 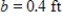
Find an equation of the parabola that models the road surface.(Assume that the origin is at the center of the road.)
Definitions:
Best Model
The most suitable statistical or computational model that provides the best fit to the data according to selected criteria.
Anova F Test
A statistical method used to compare three or more samples by analyzing the variance among them to determine if they come from the same population.
Regression Coefficients
Quantitative expressions that represent the strength and direction of the relationship between independent variables and the dependent variable in a regression analysis.
P-Value
A measure of the strength of evidence against the null hypothesis provided by a statistical test, representing the probability of observing the test results under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true.
Q21: Find the standard form of the equation
Q39: Eliminate the parameter and write the corresponding
Q90: Use the graph of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7896/.jpg" alt="Use
Q127: The following is the slope of line
Q266: Find the value of x that corresponds
Q283: The graph shows the average salaries for
Q294: Select the correct graph of the given
Q316: Find the vertex and focus of the
Q345: Using following result find a set of
Q518: Evaluate the function f(x) = 3[[3x -