The diagram below shows total revenue for a single-price monopolist.
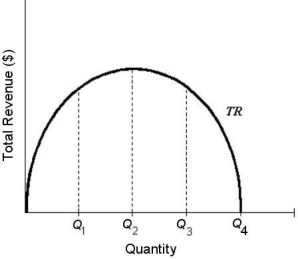 FIGURE 10-3
FIGURE 10-3
-Refer to Figure 10-3.The profit-maximizing output for this single-price monopolist is
Definitions:
Fixed Costs
Costs that do not change with the level of production or sales, including expenses like rent, salaries, and insurance.
Variable Cost
Expenses that change in proportion with production output or sales, such as materials and labor.
Fixed Costs
Costs that remain constant regardless of the amount of goods produced or sold, like lease payments, wages, and coverage fees.
Selling Price
The amount for which a good or service is sold, determining the revenue generated from sales activities.
Q3: If a union succeeds in shifting the
Q9: Suppose XYZ Corp.is producing and selling disposable
Q11: If a single-price monopolistʹs price equals marginal
Q17: One difference between a perfectly competitive market
Q24: Real capital includes<br>A)a firmʹs physical assets.<br>B)corporate bonds.<br>C)corporate
Q29: As a seller of labour services,a labour
Q36: Suppose a firm is producing 100 units
Q50: The concept of moral hazard was publicly
Q61: An economy in which there are no
Q74: In what way can an oligopolistic market