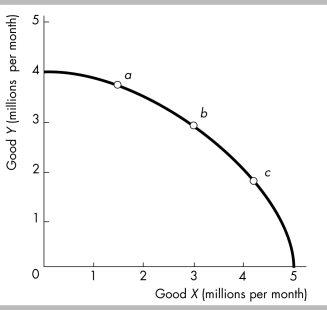
-As output moves from point a to point b to point c along the PPF in the above figure, the opportunity cost of one more unit of good X
Definitions:
Zero-Order Reaction
A chemical reaction whose rate does not change with the concentration of the reactant(s).
Reaction Rate
The speed at which a chemical reaction occurs, often influenced by factors such as temperature, concentration, and presence of catalysts.
Reaction Order
Indicates the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentration of the reactants, used to predict reaction rates.
First-Order Reaction
A chemical reaction where the rate depends linearly on the concentration of one reactant.
Q3: When a market is in equilibrium,<br>A) the
Q90: A technological improvement lowers the cost of
Q94: The opportunity cost of more capital goods
Q101: A key difference between tariffs and quotas
Q129: When the opportunity cost of producing more
Q143: For consumers, goods A and B are
Q148: Suppose the country of Atlantica imposes a
Q148: In the table above, country A is
Q189: A country possesses a comparative advantage in
Q558: Explain how price can be a regulator,