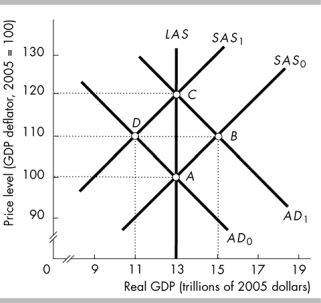
-The figure above illustrates the aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, and long-run aggregate supply in Lotus Land. The economy is currently at point D and the government increases its expenditure on goods and services. The economy will move to . The price level will_________ , and the change in real GDP will be_________ the increase in aggregate demand.
Definitions:
Fitness Program
A structured regimen or plan designed to achieve physical fitness goals, such as improving strength, flexibility, endurance, or overall health.
Population Variances
A statistical measure that represents the dispersion or spread of a set of data points in a population.
Profit Margin
A financial ratio, often expressed as a percentage, that compares a company's net income to its sales. It reveals how much profit a company makes for each dollar of its sales.
Sample Variances
The measure of spread within a sample dataset, calculated as the sum of squared deviations from the sample mean divided by the number of observations minus one.
Q42: The Employment Act of 1946 states that
Q56: The short-run Phillips curve shows the tradeoff
Q66: In the above figure, which path represents
Q89: The supply side effects of a change
Q116: Needs-tested spending _during recessions and _during expansions.<br>A)
Q199: What is the Laffer curve? Where on
Q199: For a persistent demand-pull inflation to occur,
Q247: Norway has a lower tax on dividend
Q258: A rise in the price level because
Q305: In the above figure, suppose that the