The diagrams below illustrate two alternative approaches to implementing monetary policy. The economy begins in monetary equilibrium with the interest rate equal to 2% and the money supply equal to M0.
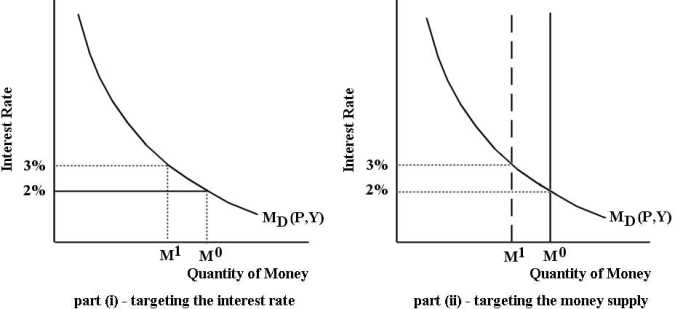 FIGURE 28-1
FIGURE 28-1
-Refer to Figure 28-1. If the Bank of Canadaʹs goal is to increase the target interest rate from 2% to 3%, then the most effective approach is to
Definitions:
Consumer Surplus
The gulf between the aggregate amount consumers are willing to allocate for a good or service and what they actually end up paying.
Producer Surplus
The variance between the minimum amount producers are prepared to take for a product and the actual payment they get.
Opportunity Cost
The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision or choosing between multiple options.
Deadweight Loss
The loss of economic efficiency that occurs when the equilibrium for a good or service is not achieved, often due to market distortions like taxes or subsidies.
Q19: Consider changes in the governmentʹs debt-to-GDP ratio.
Q25: Refer to Figure 32-2. The diagrams illustrate
Q38: If the actual unemployment rate is one
Q42: The interest rate that commercial banks charge
Q43: Consider the aggregate production function Y =
Q71: Consider a new deposit of $100 000
Q72: Which of the following correctly describes the
Q83: Refer to Table 26-2. Assume that Bank
Q118: An unemployed worker can be identified as
Q123: Consider the market for financial capital in