The diagram below shows the demand and supply curves in a perfectly competitive market.
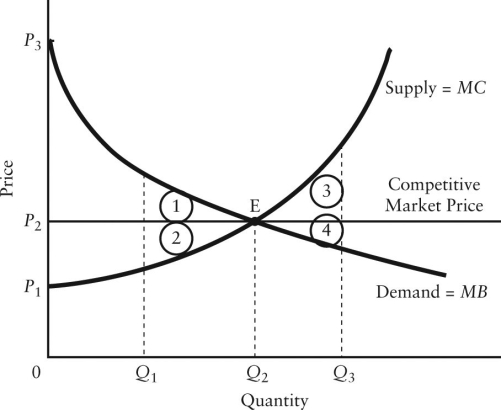 FIGURE 12-5
FIGURE 12-5
-Refer to Figure 12-5. If output in this market were Q1, but the price was still at its free-market level, the loss in consumer surplus relative to the competitive equilibrium would be illustrated by area
Definitions:
Further Processing Costs
Additional costs incurred when processing products beyond their initial production stage to enhance their value.
Selling Price
The amount a seller charges a buyer for a product or service, determined by various factors including cost, demand, and competition.
Variable Overhead Costs
Overhead costs that fluctuate with the level of production activity, such as utilities for the manufacturing plant.
Operating Capacity
The maximum output or productivity level that a company can achieve using its current resources under normal working conditions.
Q5: Which of the following statements about a
Q26: Suppose XYZ Corp. is producing and selling
Q31: Refer to Figure 13-2. This factor market
Q33: The main difference between perfect competition and
Q37: Examples of direct costs of government intervention
Q65: If a perfectly competitive firm produces at
Q88: Which of the following is a possible
Q105: The hypothesis of equal net advantage explains
Q118: A perfectly competitive firmʹs total revenue is
Q125: Private and competitive markets could produce efficient